Transparent Model of the Mirage F1 Fighter (Le Bourget)
The Mirage F1 supersonic fighter was a further development of the Mirage III and made its first flight on December 23, 1966. Adopted by the French Air Force in 1973, it was also delivered to a dozen countries, including Spain, Greece, Iraq, Qatar, and Morocco.
Aircraft length 15 m, height 4.5 m, wingspan 8.40 m, wing area: 29 m2. Maximum speed 2335 km / h, practical ceiling 20000 m. Empty weight 7,400 kg, maximum take-off weight 16,200 kg, flight range with a maximum combat load of 900 km.
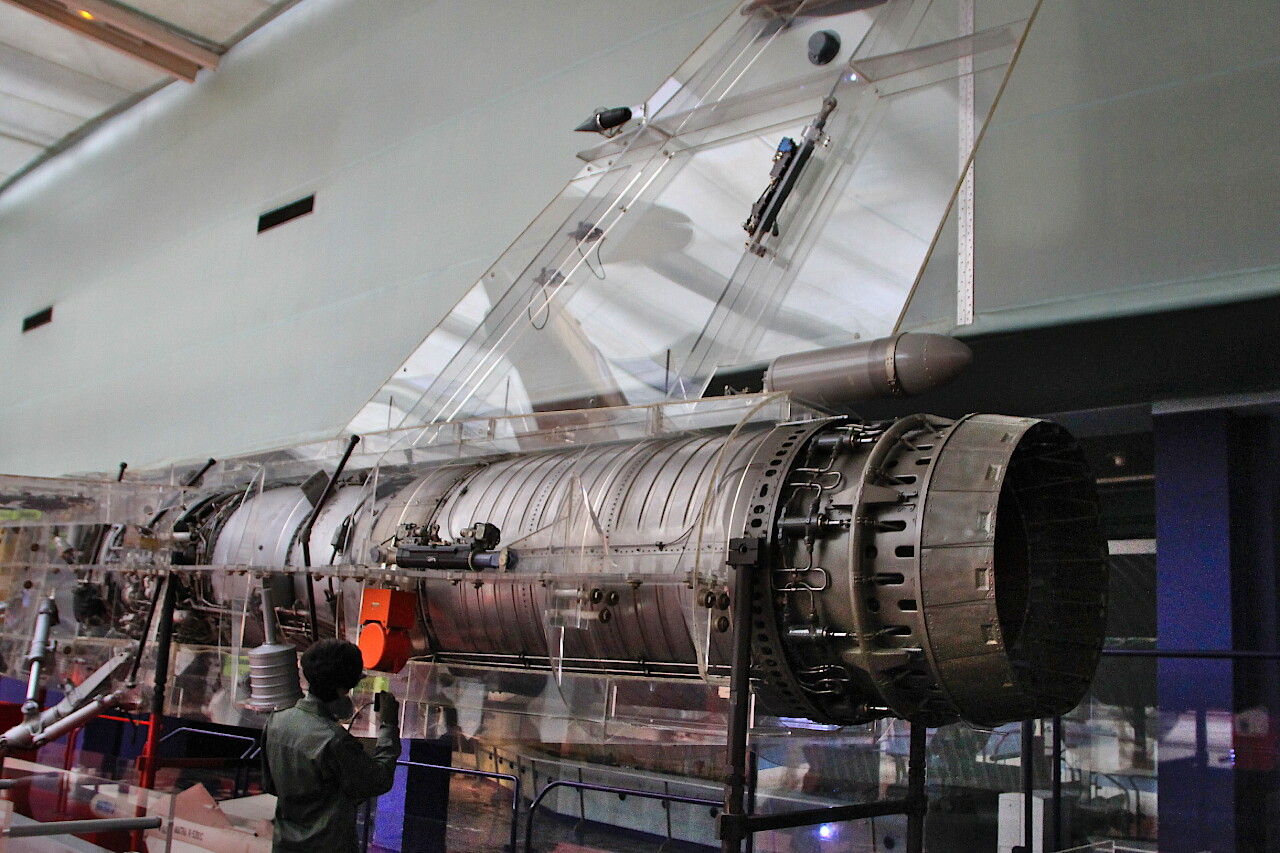

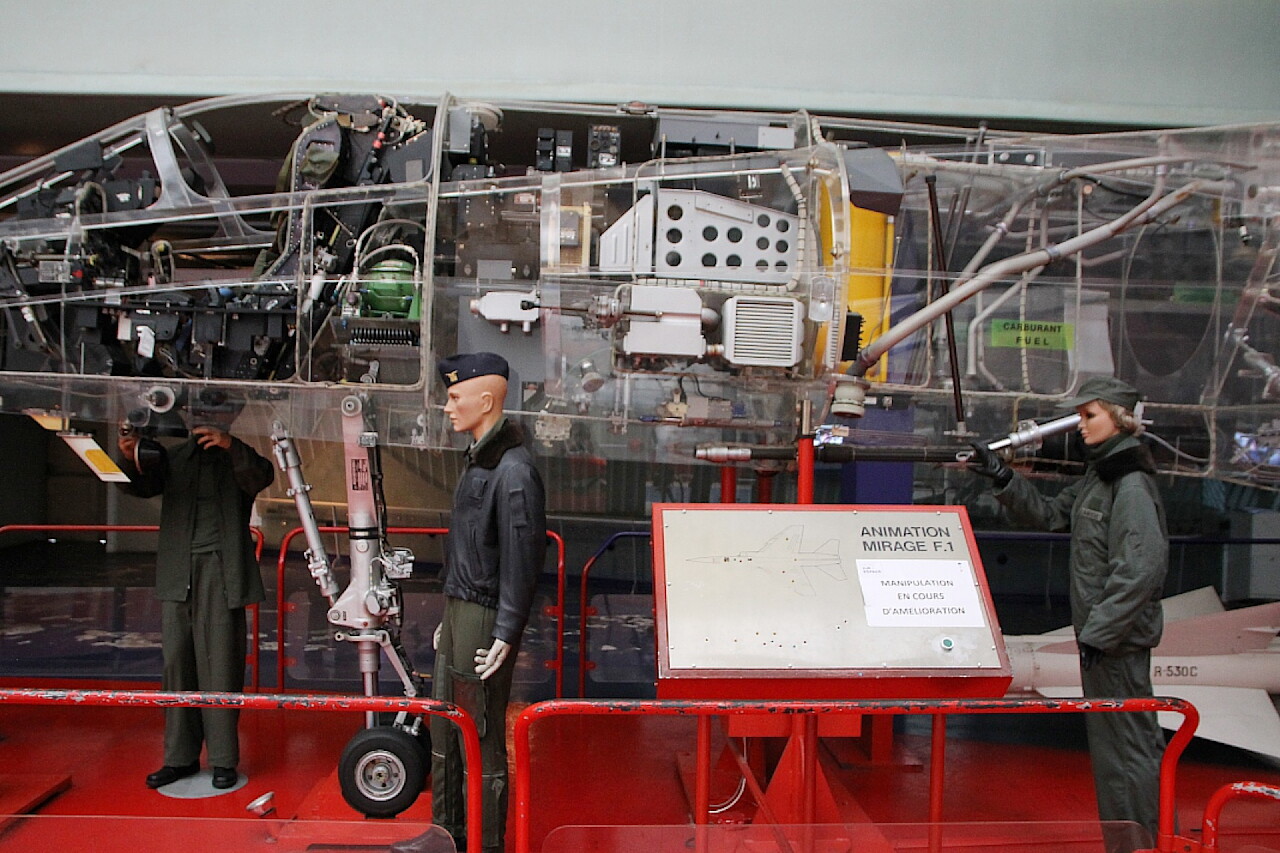
The Le Bourget Museum presents a model Mirage F1. C made of transparent plastic, in which the equipment of a real aircraft is installed. It was made for the Paris Air Show in 1977, then participated in other exhibitions, taking a place in the museum in 1979.

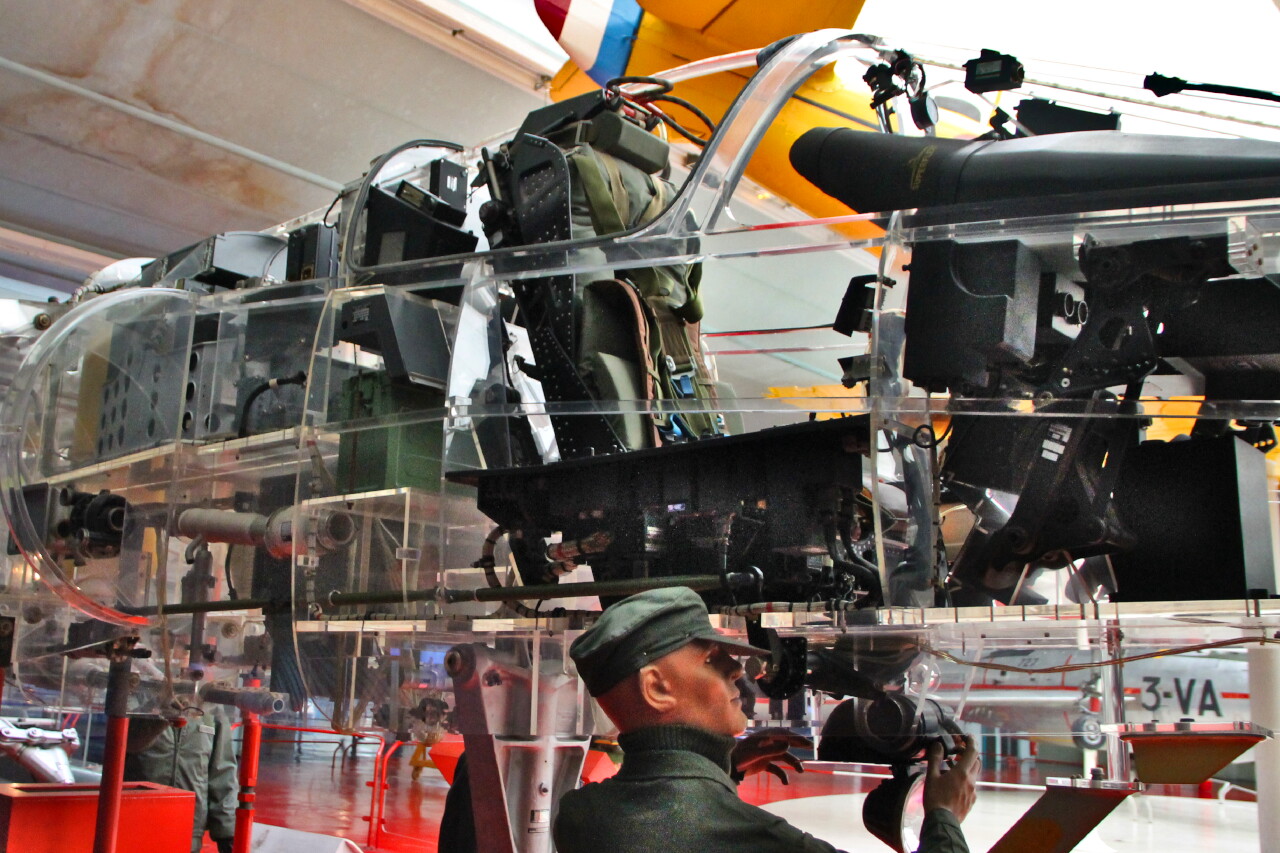
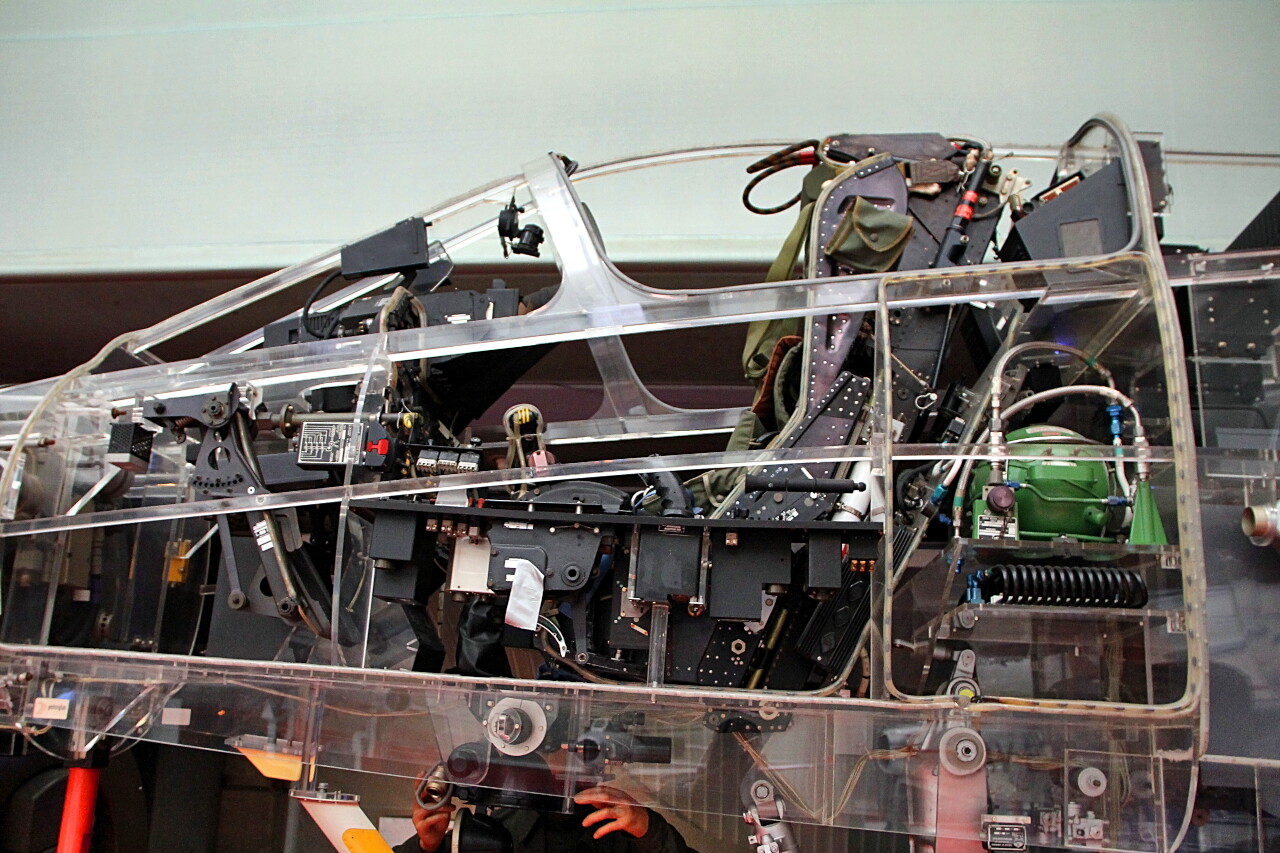
The key difference between the Mirage F1 and its predecessors was avionics. On-board electronic equipment occupies a significant amount of space in the front and rear of the cockpit.

In the bow, a powerful radar system is installed, covered with a radio-transparent fairing.
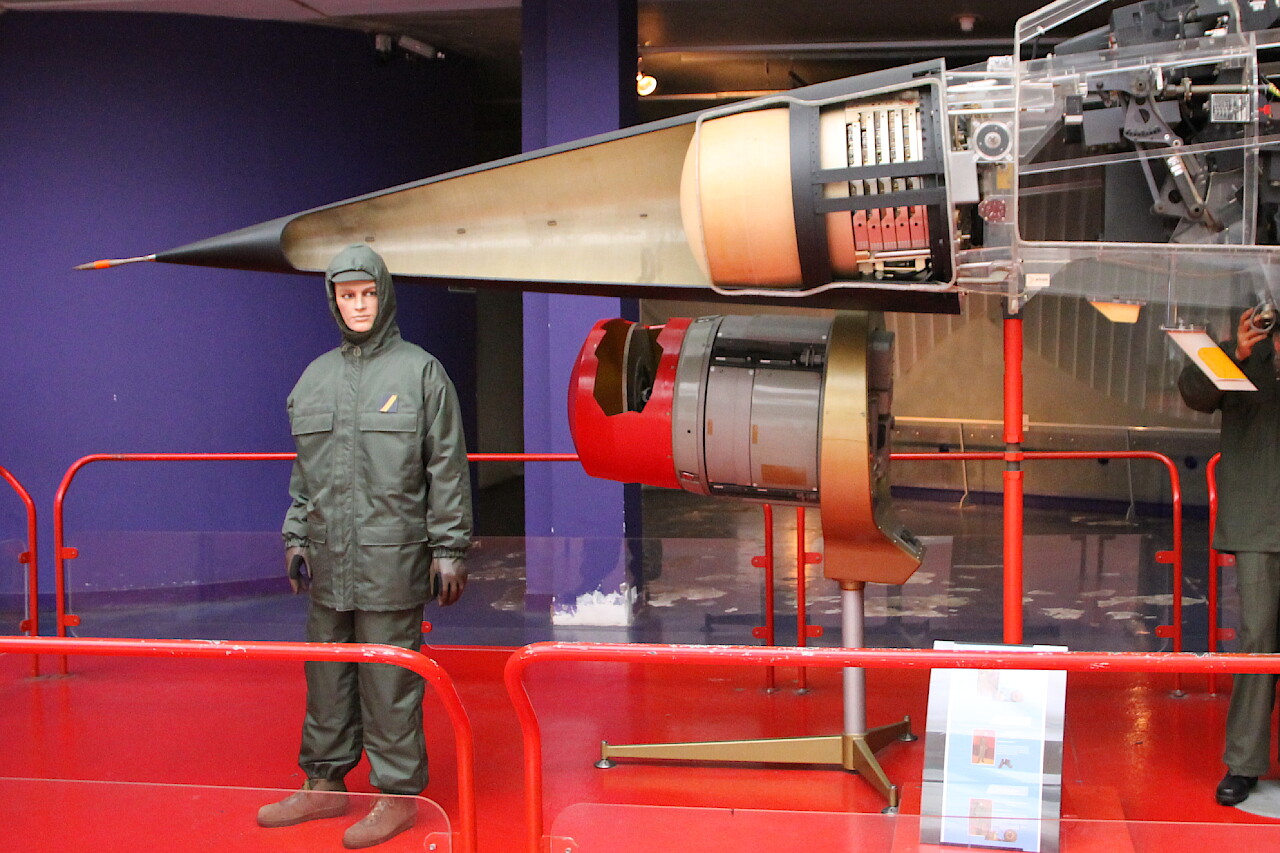

The Thomson-CSF Cyrano IV radar performs several functions and can operate in three modes: detection and tracking of air targets, providing flight with rounding terrain, and when performing reconnaissance missions, the terrain mapping function is used.
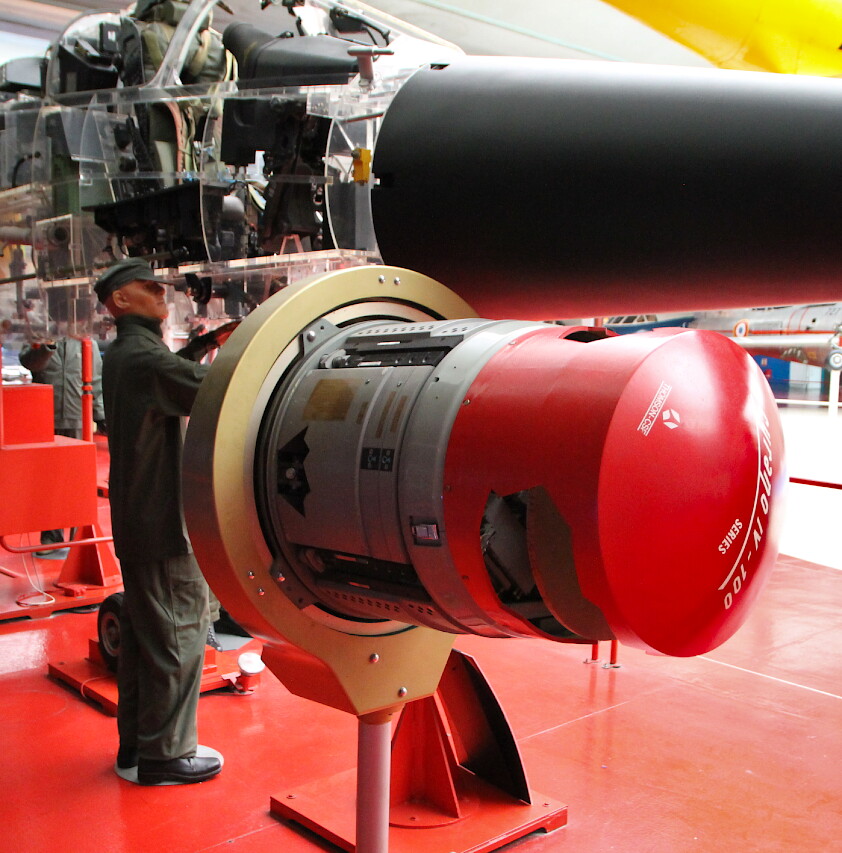

The Cyrano IV radar was capable of detecting aerial targets at twice the range of previous models.
The standard production Mirage F1 includes a radio altimeter, an SFENA 505 autopilot with yaw damper, an inertial navigation system, an instrument landing system (ILS), a friend-or-foe answering machine, UHF/VHF radio stations, a TACAN tactical air navigation system, and data transmission equipment to the ground command post.
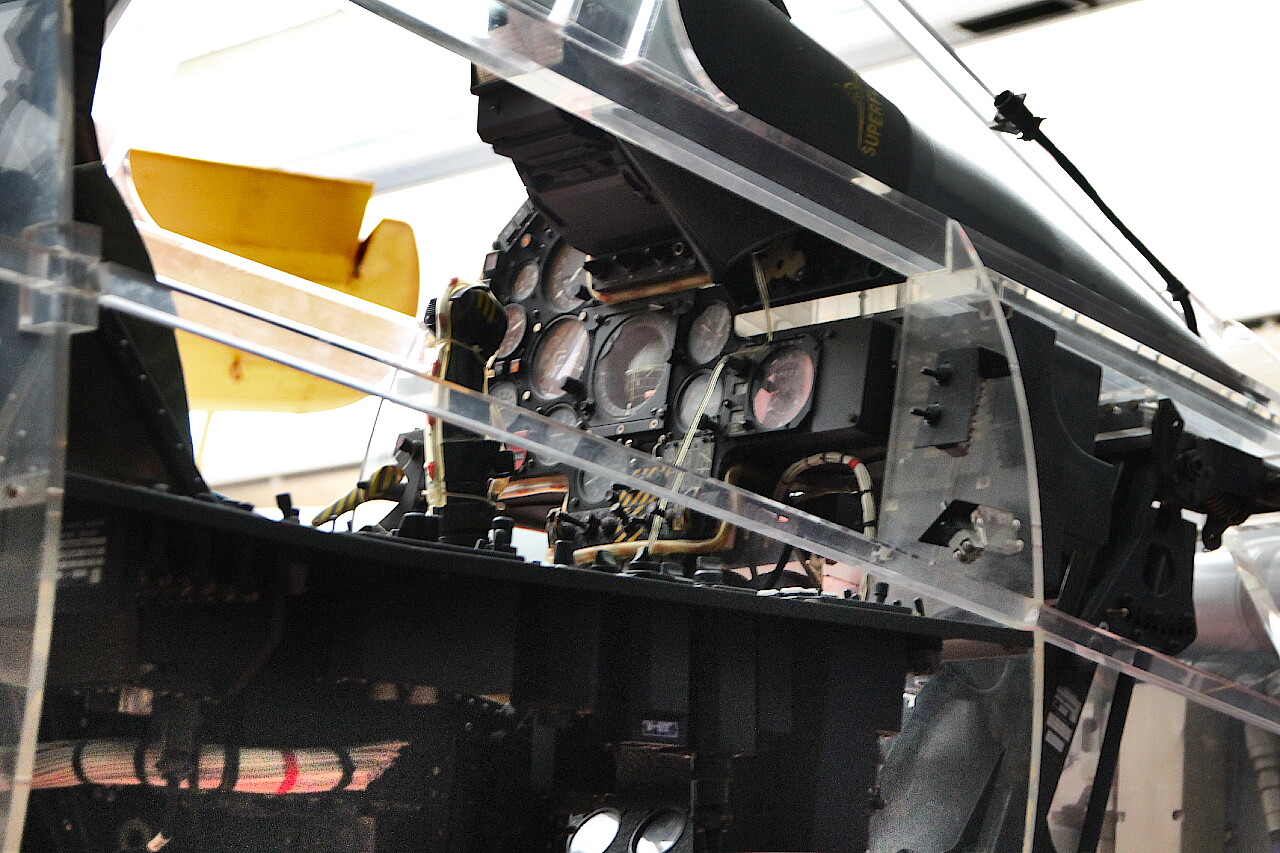
The most important element of the pilot's cabin is the ejection seat. It provides comfortable operation during the flight and rescue of the pilot in case of aircraft damage.

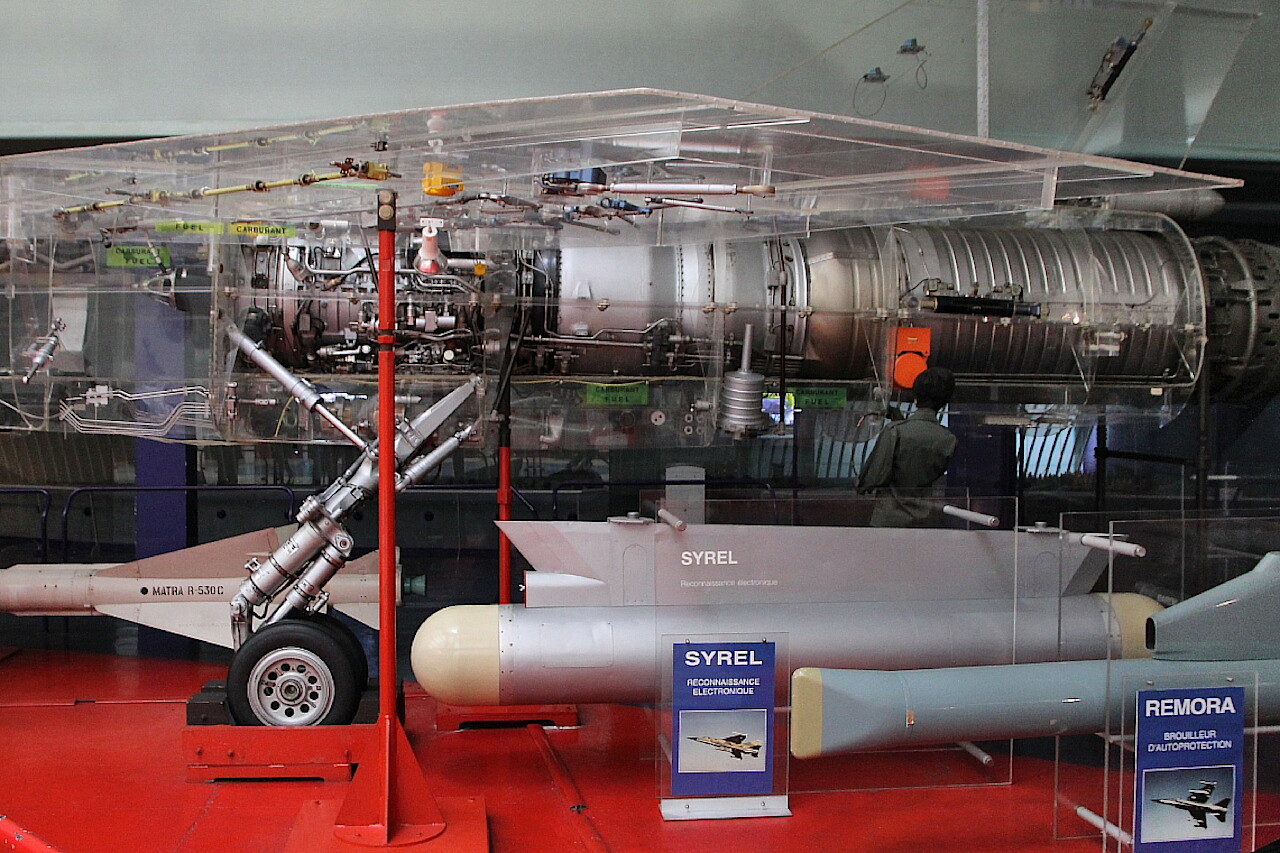
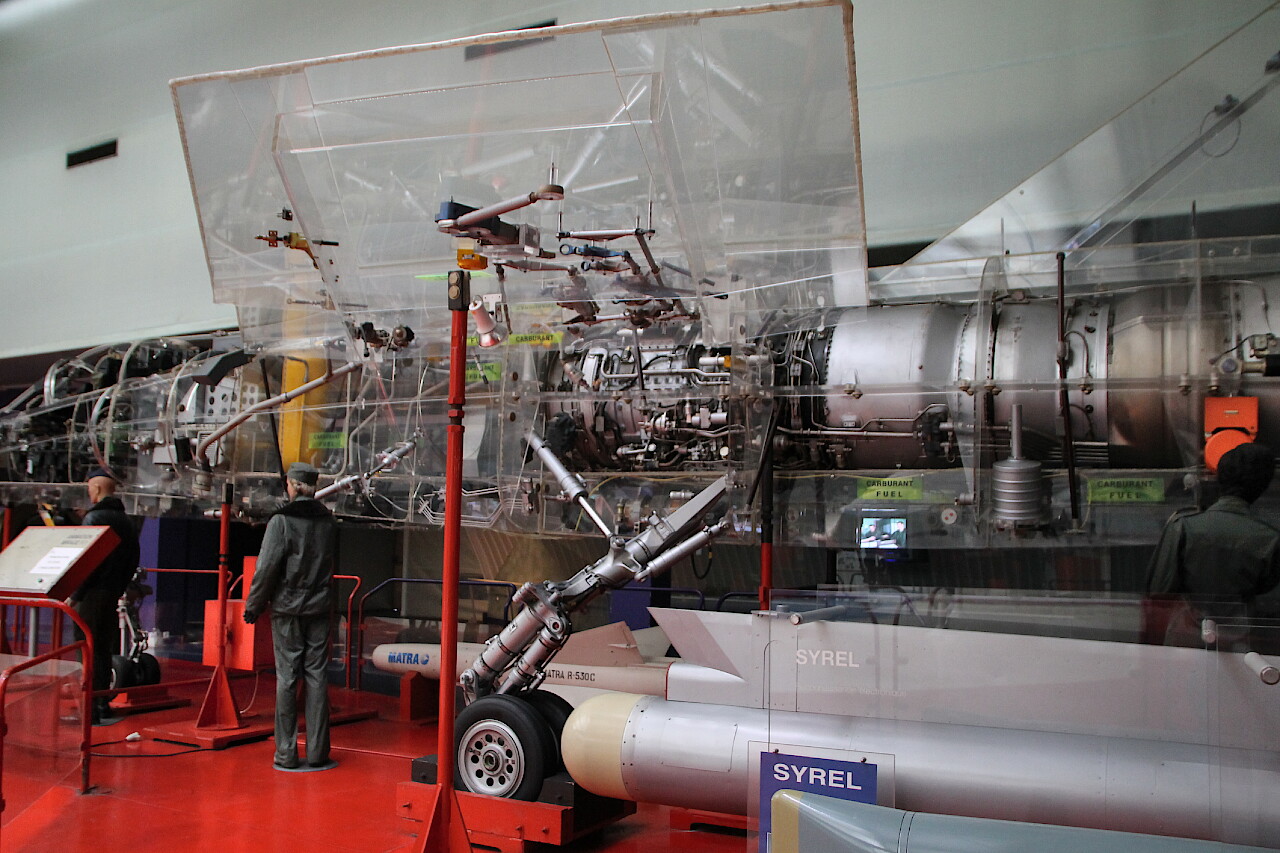
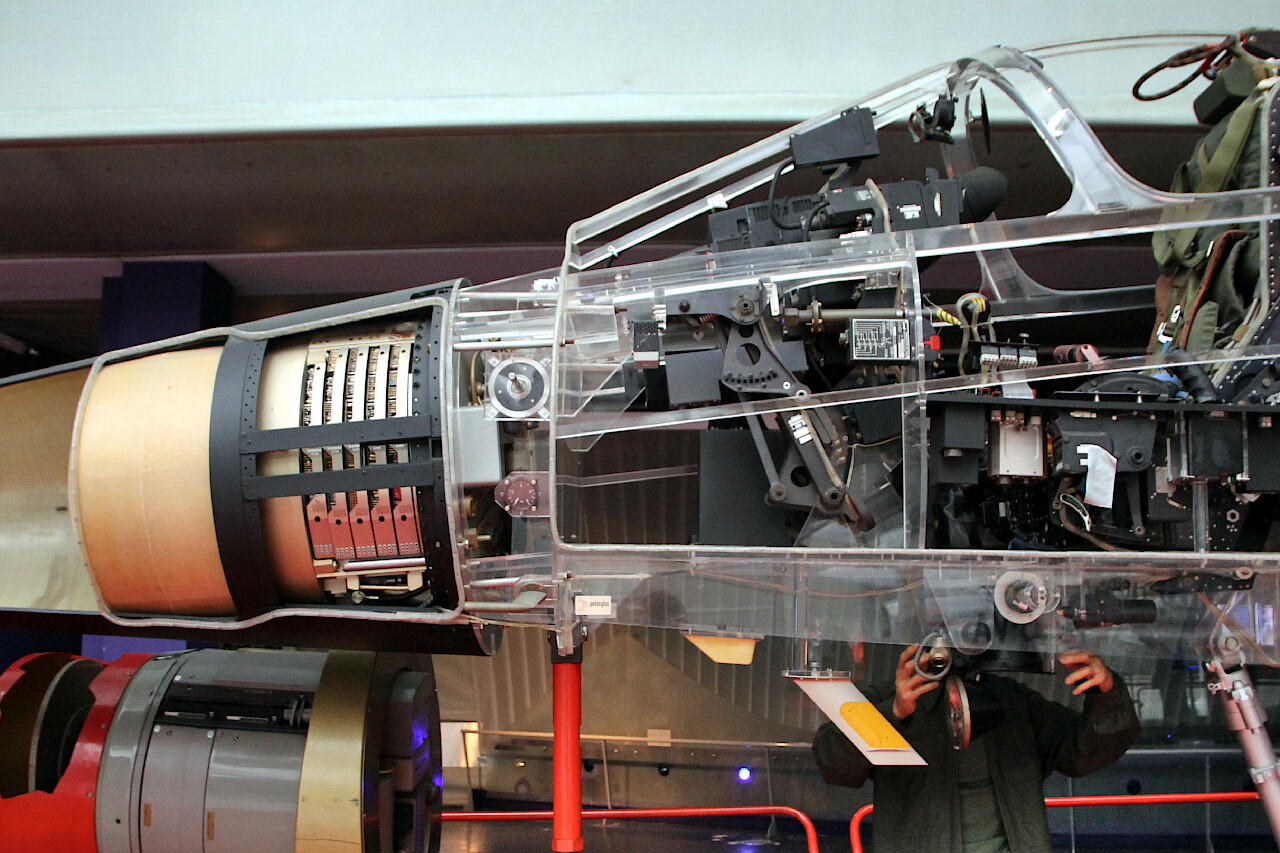
The aircraft is equipped with a SNECMA Atar 9K-50 turbojet engine with a thrust of 7200 kg.
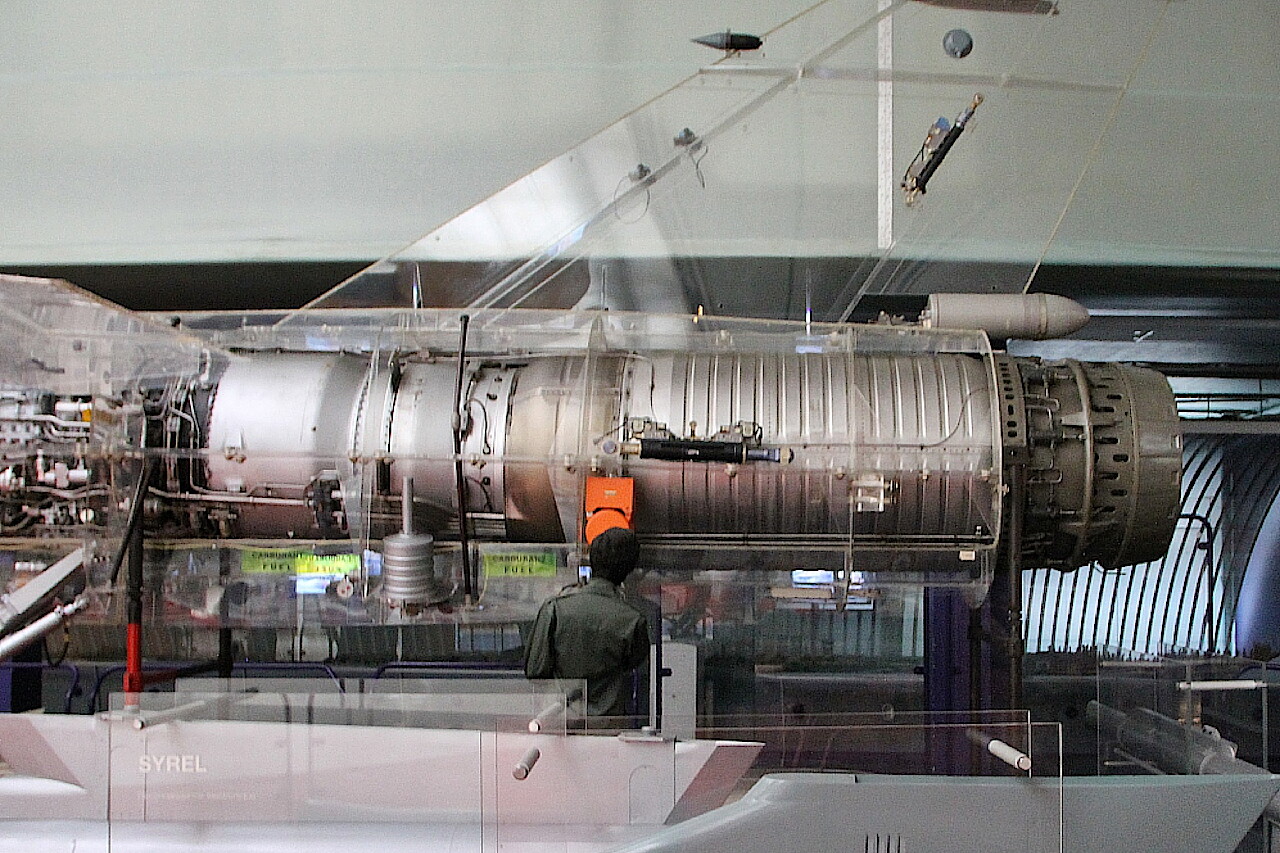
This engine was first tested in 1948 and, constantly improving, is still used today.
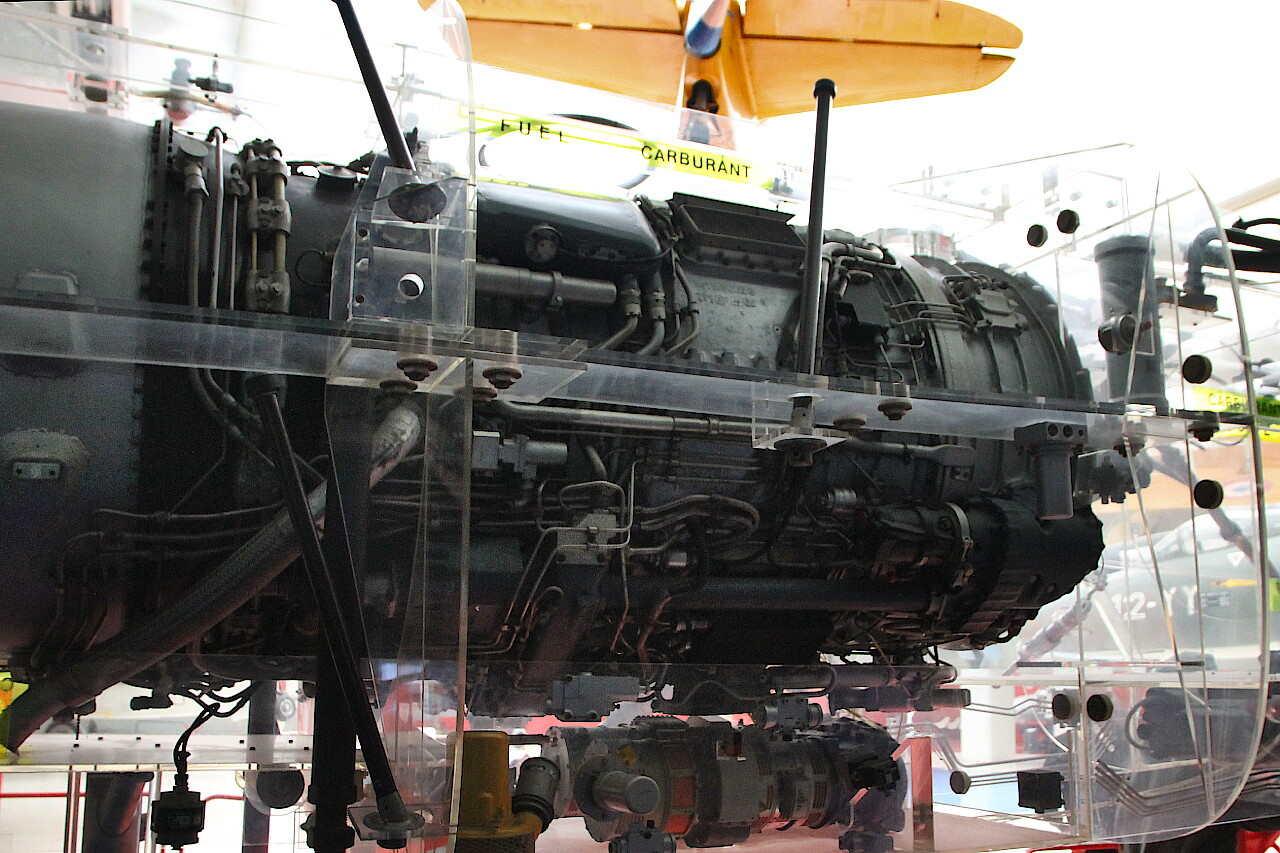

As you can see, it occupies almost half of the fuselage, behind the turbine is a large afterburner. The main fuel tank is located in front of the engine.
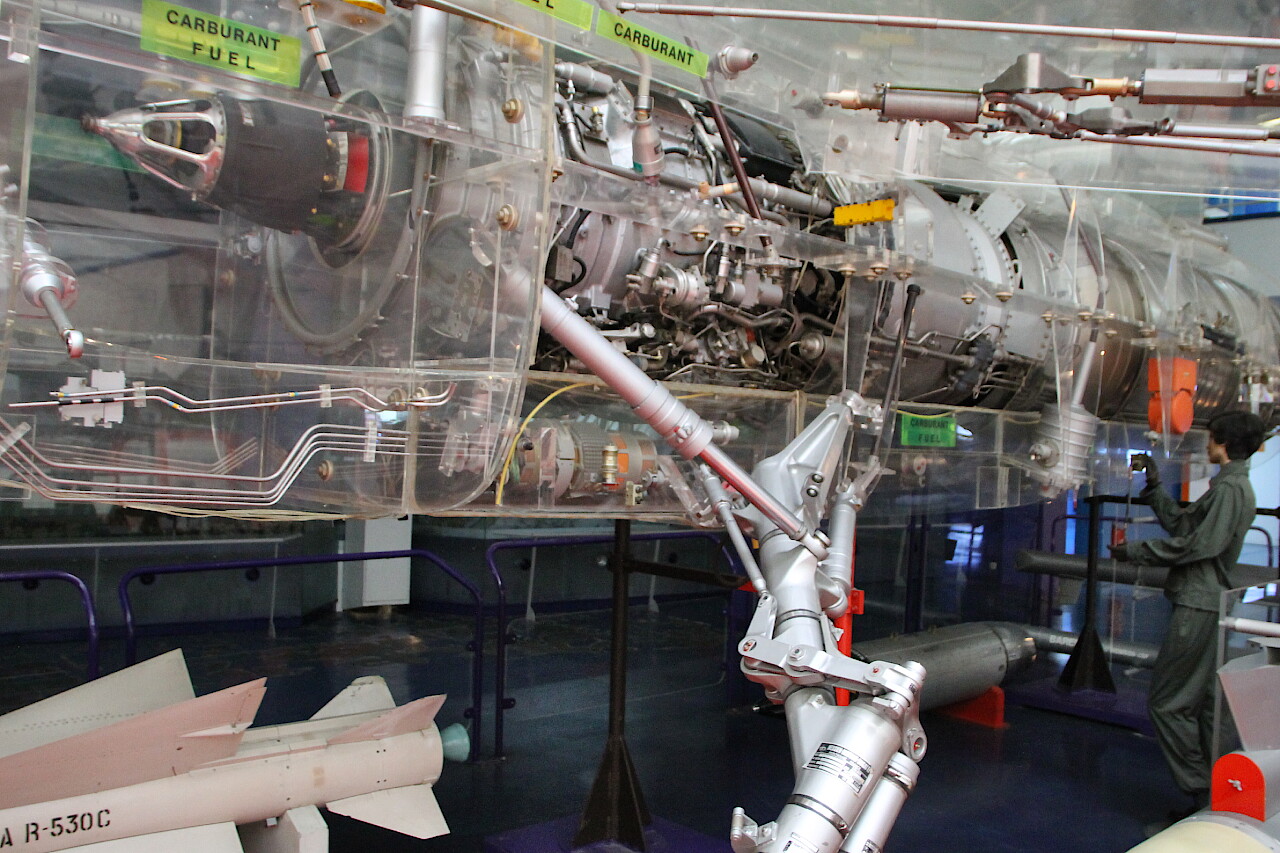
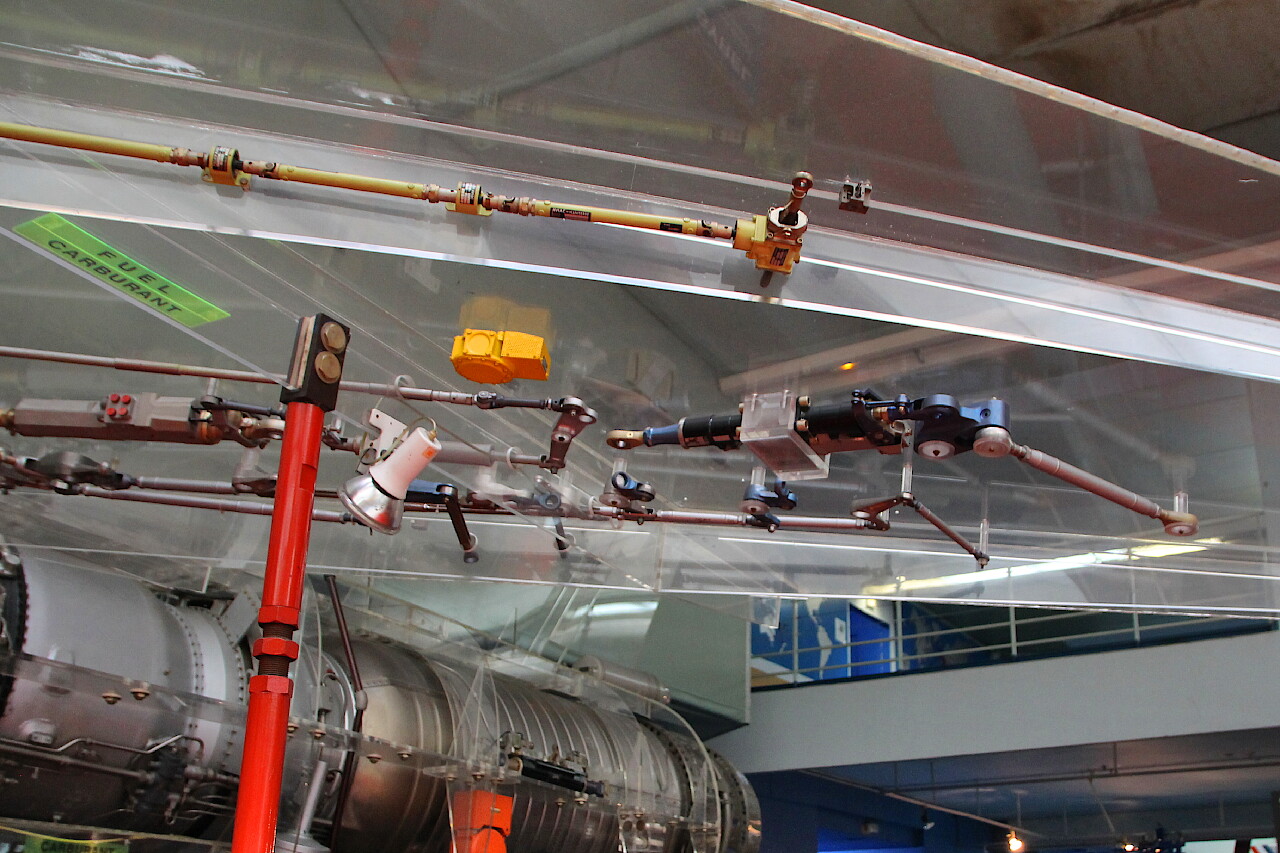
On the transparent wings, you can view the device of the wing mechanization system.

Next to the layout are some samples of weapons that the aircraft can carry. These are the Matra R-530 C air-to-air missile, a container with Syrel reconnaissance electronic equipment and a Thomson-CSF Remora radar silencer.