T26, Soviet Light Infantry Tank
In the twenties, the main tank of the Red Army of the USSR was the light T-18, which was a modernized French Renault FT modèle 1917 of the end of the First World War. By the end of the decade, it did not meet the needs of the General Staff at all, and Soviet designers could not offer any worthy replacement. Therefore, on December 5, 1929, the State Commission for heavy Engineering decided to study foreign experience in order to select a suitable prototype for setting up its production in the USSR. In the spring of 1930, the commission chose the British Vickers Mk.E tank (another name for the Vickers 6-ton). The tank was developed in 1928 under the supervision of famous designers John Valentine Carden and Vivian Loyd.
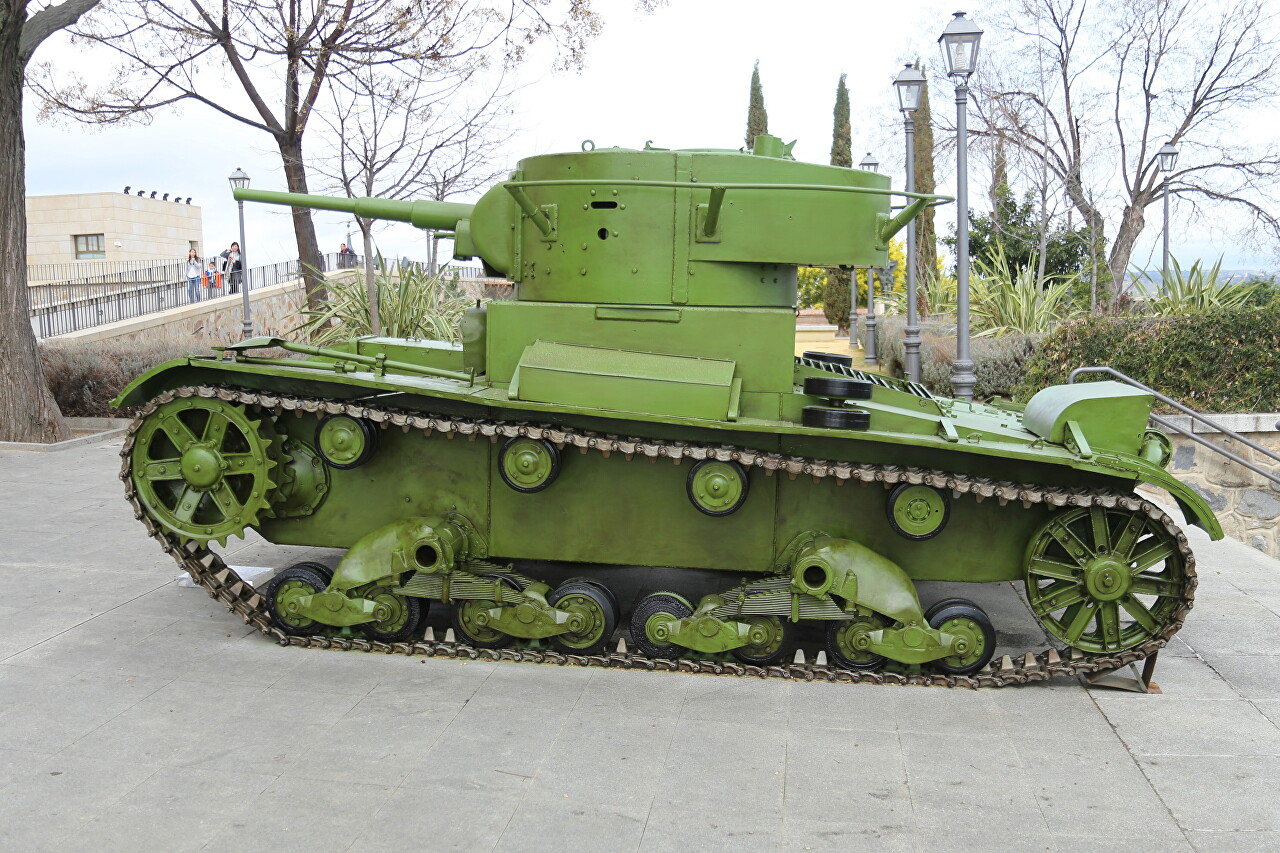

The tank's hull was riveted from 1-inch and 3/4-inch thick steel sheets, and the 80-95 horsepower Armstrong Siddeley engine allowed for a top speed of 22 mph (35 km/h) on paved roads. The Horstmann suspension with two spring-loaded two-wheeled bogies on board provided good cross-country performance. The high-strength steel tracks provided a service life of more than 3,000 miles (4,800 km). Although Mk.The E was superior to most designs of the time, but was not adopted in the UK, so it was offered for export. I must say that the UK at that time was the world leader in the production of tanks, all other manufacturers somehow repeated their designs. The Vickers-Amrstrong company offered two models: with two 7.71 mm machine guns in two turrets (Type A) and with a 47 mm cannon and a 7.71 mm machine gun in one turret (Type B). Soviet specialists were interested only in the machine-gun modification, but an attempt to buy one prototype with technical documentation failed. As a result of negotiations, a contract was signed for the purchase of 15 units of each modification, as well as a license and documentation for the production of Mk.Under the terms of the contract, Soviet specialists also got acquainted with the production technology of these tanks at the company's plant. The first British-built tanks arrived in the USSR at the end of the 30 year and entered military testing under the name B (Vickers) -26. In January 1931, it became known that Poland had also acquired tanks of this type. Since the 1920s, independent Poland was considered the main enemy of the USSR, so it was decided to start mass production before the tests were completed. On February 13, the T-26 was adopted as the main tank of direct support for combined arms units and tank units of the Supreme Command reserve.

In total, up to 1941, more than 11,000 units were produced, this is the largest tank series in the world during the interwar period. During the production process in the USSR, 53 prototypes were developed based on the T-26, including flamethrower tanks, self-propelled artillery units, sapper vehicles, artillery tractors and armored personnel carriers, and even radio-controlled tanks without a crew. 23 modifications were put into service. The tank was reliable and easy to maintain, and played a significant role in the Battle of Lake Hassan in 1938, as well as in the Winter War of 1939-40. The T-26 was exported and performed well during the Spanish Civil War. China and Turkey were also among the buyers. Captured T-26s were used by the Finnish, German, Romanian and Hungarian armies. By the beginning of World War II, the T-26 was already obsolete, and the armor did not protect against anti-tank artillery, at the time of the German invasion in June 1941, it was the most numerous tank in the Red Army. T-26s took part in the Battle of Moscow in 1941-42, in the Battle of Stalingrad and the Battle for the Caucasus in 1942-1943, On the Leningrad front, T-26s were used until 1944. The last time the USSR used the T-26 was in August 1945, during the defeat of the Japanese Kwantung Army in Manchuria. China used the T-26 until 1949.

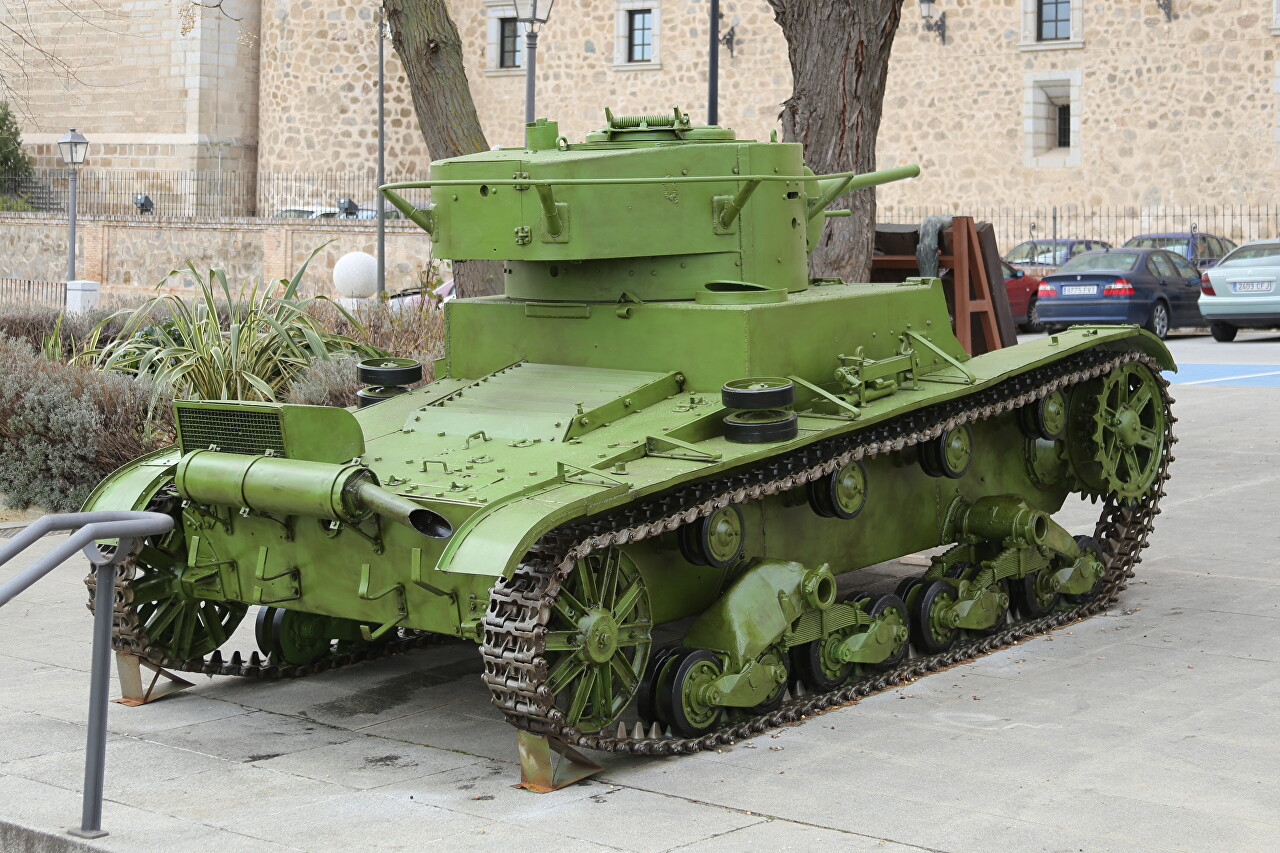
The Alcazar Museum in Toloedo presents one of the T-26s produced in 1933. The Republican Army of Spain received 281 tanks from the USSR, they participated in all major battles of the Civil War. The first 50 units were delivered to Cartagena on September 15, 1936, and in October they already took part in the battles of Toledo. This tank was captured by the Nationalist army and after the war became part of the First Spanish Armored Brigade.

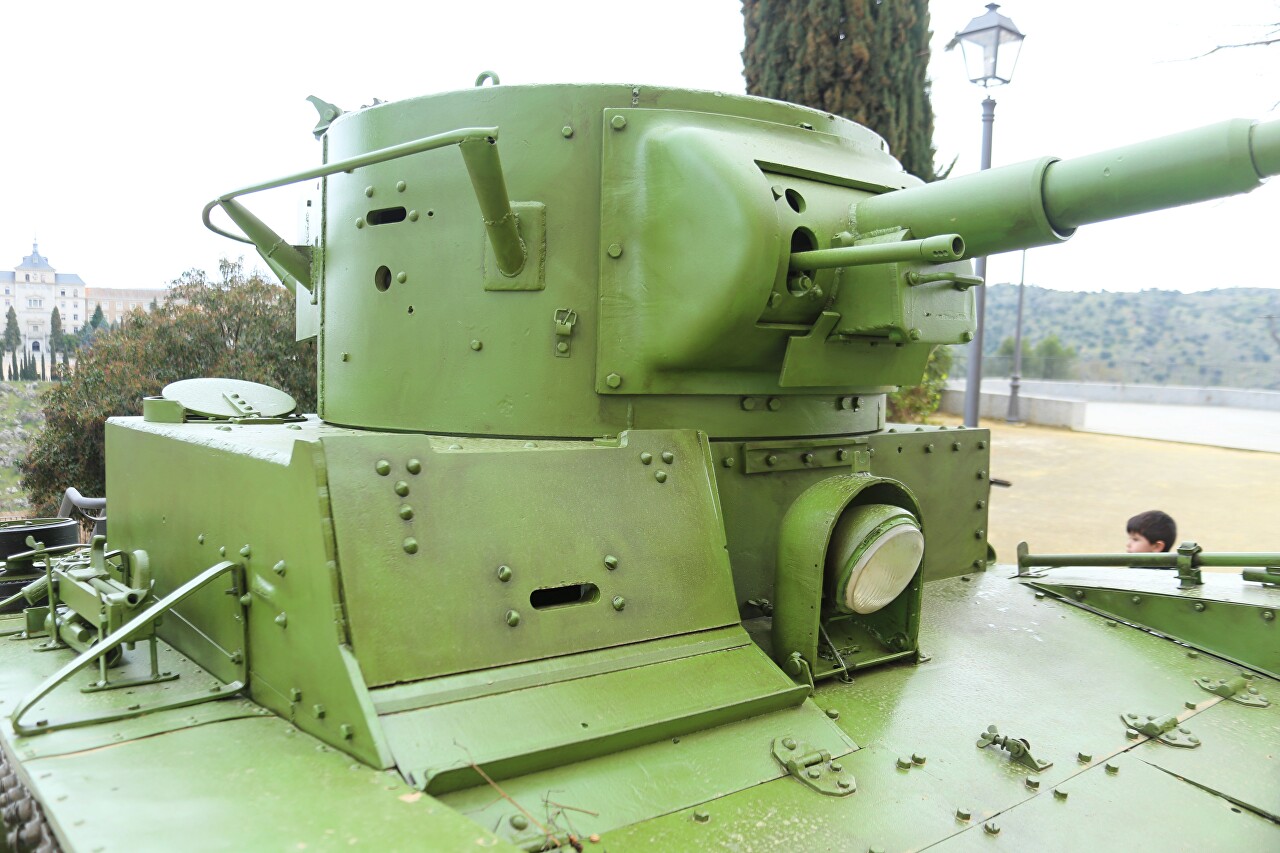
Characteristics of the T-26 tank: Body length 4620 mm, width 2445 mm, height 2330 mm, ground clearance 380 mm. combat weight 10.28 tons. The tank had a four-cylinder carburetor air-cooled GAZ T-26 engine (a copy of Armstrong Siddeley) on early models had a power of 74 hp and low reliability, after 1934 the quality improved, and the power was brought to 90 hp like the British original. Maximum speed of 30 km / h, driving range on the road 225 km, off-road 175 km. Armament: 40 mm semi-automatic gun 20-K with a barrel length of 46 calibers and ammunition of 122 rounds. 7.62 mm DT machine gun with a reserve of 2961 shots. The crew consists of 3 people. The handrail around the tower served as a radio antenna, but only the commander's tanks had a radio station, and even then not all of them. Commands to Soviet tankers were given by flags before the battle, most often the commander sent the command "Do as I do", there was no coordination between the tanks in the battle.

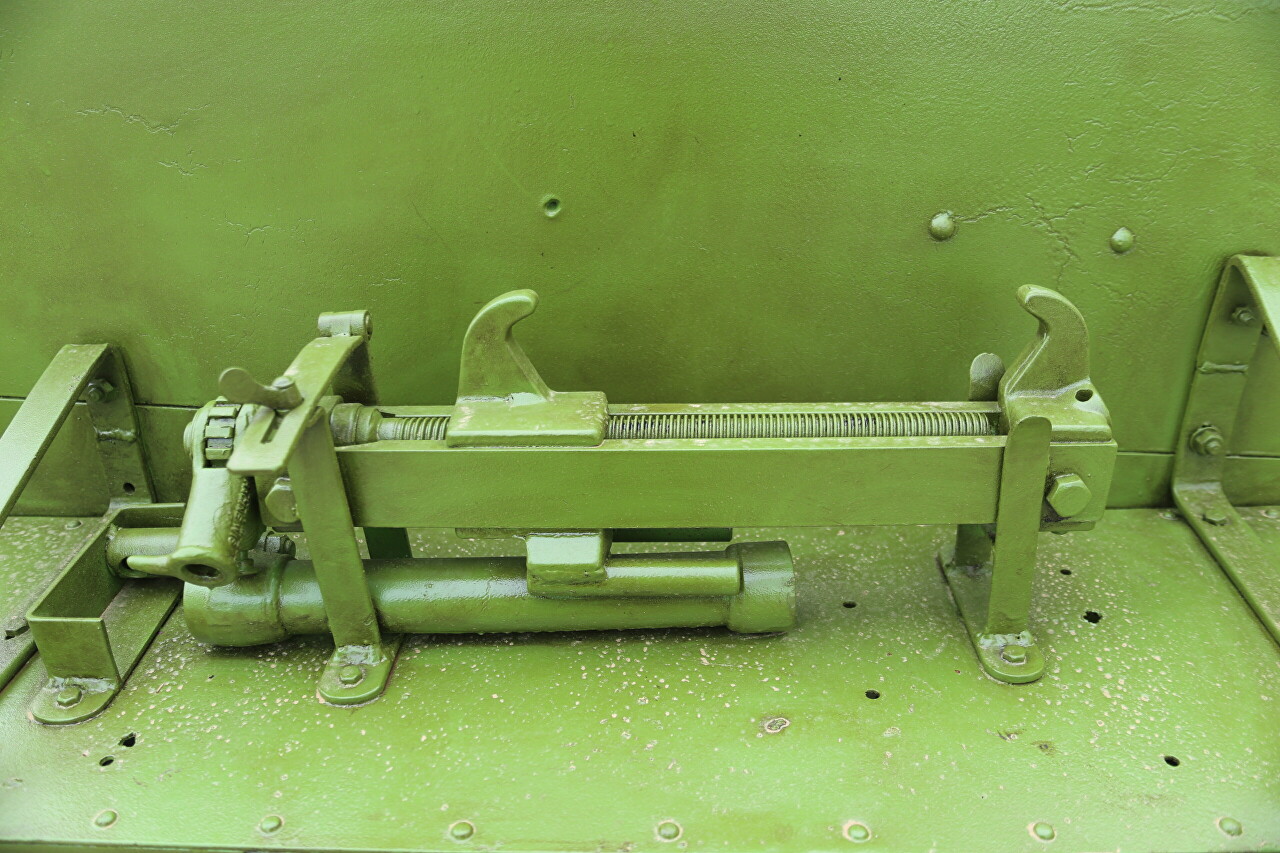
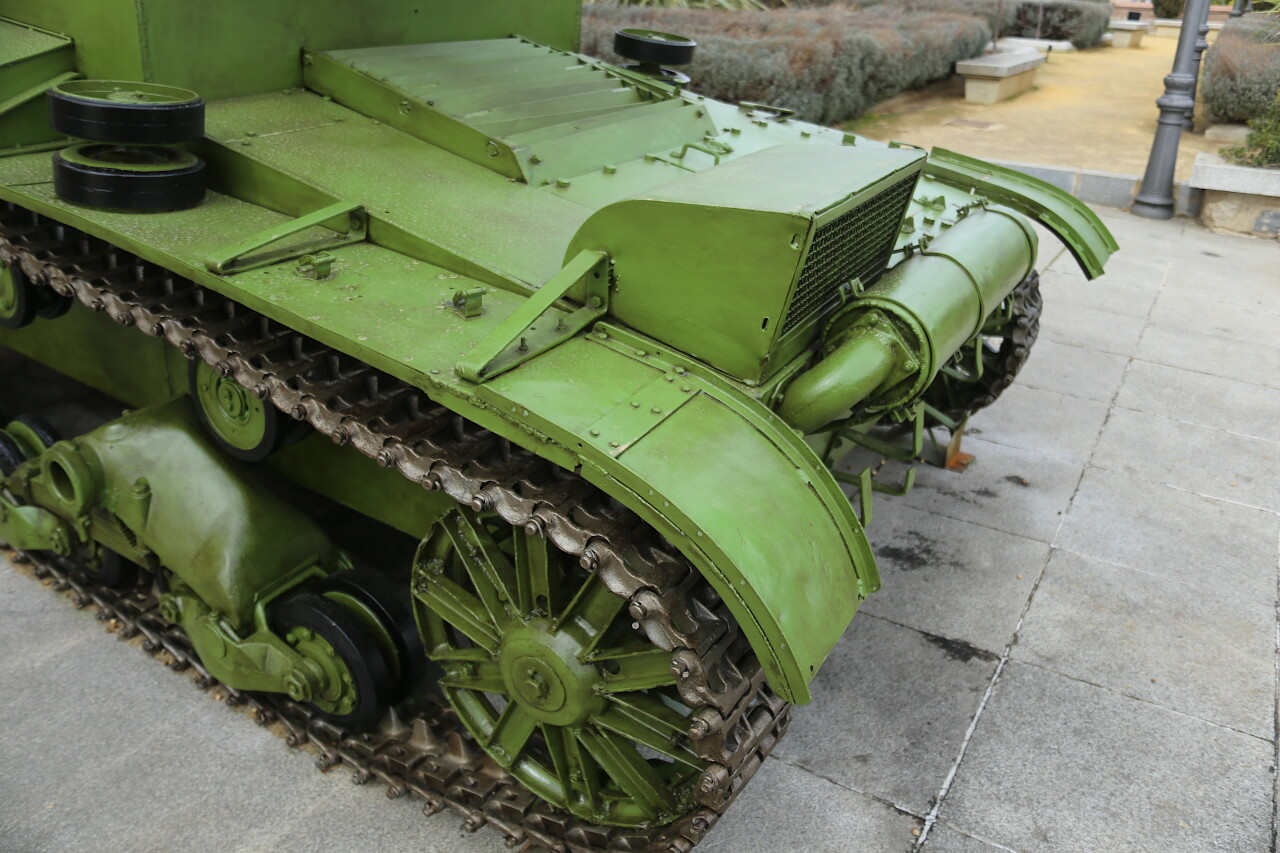
I've been puzzling over what kind of device it is. But then I realized that it was a device for pulling the tracks together after a break. I want to say that I've seen a lot of tanks, but this is the first time I've seen such a tool.